In this project, students will create a basic calculator application in Python capable of performing four basic arithmetic operations: addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. This project will introduce you to essential programming concepts such as functions, conditional statements, input/output, and exception handling, making it an ideal starting point for beginners.
Create a New Python File: Start by creating a new Python file (e.g., calculator.py) in your IDE or text editor.
Define the Basic Functions: First, we will define functions for each of the arithmetic operations.
# Function for addition
def add(x, y):
return x + y
# Function for subtraction
def subtract(x, y):
return x - y
# Function for multiplication
def multiply(x, y):
return x * y
# Function for division
def divide(x, y):
if y == 0:
return "Error! Division by zero."
else:
return x / y
Display the Menu to the User: Now, let’s create a simple menu for the user to choose the operation they want to perform.
# Displaying the operation menu
def print_menu():
print("Select operation:")
print("1. Add")
print("2. Subtract")
print("3. Multiply")
print("4. Divide")
Take User Input: After displaying the menu, ask the user for input and handle invalid inputs appropriately.
def get_input():
try:
# Get the user's choice of operation
choice = int(input("Enter choice (1/2/3/4): "))
# Check if the choice is valid
if choice not in [1, 2, 3, 4]:
print("Invalid input, please enter a number between 1 and 4.")
return None, None, None
else:
# Get the numbers for the calculation
num1 = float(input("Enter first number: "))
num2 = float(input("Enter second number: "))
return choice, num1, num2
except ValueError:
print("Invalid input! Please enter valid numbers.")
return None, None, None
Perform the Operation Based on User Input: Use a loop to allow the user to perform multiple calculations, and process their input using if-else conditions.
def calculate():
while True:
# Display the menu
print_menu()
# Get user choice and numbers
choice, num1, num2 = get_input()
if choice is None:
continue
# Perform the calculation based on user's choice
if choice == 1:
print(f"{num1} + {num2} = {add(num1, num2)}")
elif choice == 2:
print(f"{num1} - {num2} = {subtract(num1, num2)}")
elif choice == 3:
print(f"{num1} * {num2} = {multiply(num1, num2)}")
elif choice == 4:
print(f"{num1} / {num2} = {divide(num1, num2)}")
# Ask if the user wants to perform another operation
next_calculation = input("Do you want to perform another calculation? (yes/no): ")
if next_calculation.lower() != 'yes':
print("Exiting the calculator. Goodbye!")
break
Run the Program: Finally, execute the program by calling the calculate() function.
if __name__ == "__main__":
calculate()
Full Code:
# Function for addition
def add(x, y):
return x + y
# Function for subtraction
def subtract(x, y):
return x - y
# Function for multiplication
def multiply(x, y):
return x * y
# Function for division
def divide(x, y):
if y == 0:
return "Error! Division by zero."
else:
return x / y
# Displaying the operation menu
def print_menu():
print("Select operation:")
print("1. Add")
print("2. Subtract")
print("3. Multiply")
print("4. Divide")
# Taking user input and handling exceptions
def get_input():
try:
# Get the user's choice of operation
choice = int(input("Enter choice (1/2/3/4): "))
# Check if the choice is valid
if choice not in [1, 2, 3, 4]:
print("Invalid input, please enter a number between 1 and 4.")
return None, None, None
else:
# Get the numbers for the calculation
num1 = float(input("Enter first number: "))
num2 = float(input("Enter second number: "))
return choice, num1, num2
except ValueError:
print("Invalid input! Please enter valid numbers.")
return None, None, None
# Performing the operation
def calculate():
while True:
# Display the menu
print_menu()
# Get user choice and numbers
choice, num1, num2 = get_input()
if choice is None:
continue
# Perform the calculation based on user's choice
if choice == 1:
print(f"{num1} + {num2} = {add(num1, num2)}")
elif choice == 2:
print(f"{num1} - {num2} = {subtract(num1, num2)}")
elif choice == 3:
print(f"{num1} * {num2} = {multiply(num1, num2)}")
elif choice == 4:
print(f"{num1} / {num2} = {divide(num1, num2)}")
# Ask if the user wants to perform another operation
next_calculation = input("Do you want to perform another calculation? (yes/no): ")
if next_calculation.lower() != 'yes':
print("Exiting the calculator. Goodbye!")
break
# Running the program
if __name__ == "__main__":
calculate()
Conclusion:
By completing this project, you will have gained hands-on experience with Python functions, conditional statements, input/output handling, and exception handling. These are all essential skills that will serve as a foundation for more complex programming projects.
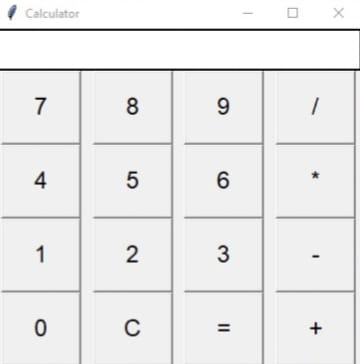
Creating a simple calculator using Python's Tkinter module is an excellent way to learn how to build GUIs. Below is a step-by-step guide to create a basic calculator, along with an explanation of each part of the program.
Import Required Libraries:
Set Up the Main Window:
Create the Display Field:
Create the Buttons:
Define Functions:
Run the Application:
import tkinter as tk
# Function to update the display when buttons are clicked
def button_click(value):
current = entry.get()
entry.delete(0, tk.END) # Clear the current display
entry.insert(0, current + value) # Insert the clicked value
# Function to clear the display
def button_clear():
entry.delete(0, tk.END)
# Function to evaluate the expression and display the result
def button_equal():
try:
result = str(eval(entry.get())) # Evaluate the expression in the entry
entry.delete(0, tk.END)
entry.insert(0, result) # Show result in the display
except:
entry.delete(0, tk.END)
entry.insert(0, "Error") # In case of an error (invalid expression)
# Create the main window
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("Calculator")
# Create an entry widget to show the input and result
entry = tk.Entry(root, width=20, font=("Arial", 24), borderwidth=2, relief="solid")
entry.grid(row=0, column=0, columnspan=4)
# Create buttons for digits and operators
buttons = [
('7', 1, 0), ('8', 1, 1), ('9', 1, 2), ('/', 1, 3),
('4', 2, 0), ('5', 2, 1), ('6', 2, 2), ('*', 2, 3),
('1', 3, 0), ('2', 3, 1), ('3', 3, 2), ('-', 3, 3),
('0', 4, 0), ('C', 4, 1), ('=', 4, 2), ('+', 4, 3)
]
# Create and place each button
for (text, row, col) in buttons:
if text == "=":
button = tk.Button(root, text=text, width=5, height=2, font=("Arial", 18), command=button_equal)
elif text == "C":
button = tk.Button(root, text=text, width=5, height=2, font=("Arial", 18), command=button_clear)
else:
button = tk.Button(root, text=text, width=5, height=2, font=("Arial", 18), command=lambda value=text: button_click(value))
button.grid(row=row, column=col)
# Start the main loop to run the application
root.mainloop()
Explanation of the Program:
Imports:
Functions:
Creating the Window:
Display:
Buttons:
Placing the Buttons:
Main Loop:
This program creates a basic, functional calculator that performs arithmetic operations.





Looking for more job opportunities? Look no further! Our platform offers a diverse array of job listings across various industries, from technology to healthcare, marketing to finance. Whether you're a seasoned professional or just starting your career journey, you'll find exciting opportunities that match your skills and interests. Explore our platform today and take the next step towards your dream job!
Looking for insightful and engaging blogs packed with related information? Your search ends here! Dive into our collection of blogs covering a wide range of topics, from technology trends to lifestyle tips, finance advice to health hacks. Whether you're seeking expert advice, industry insights, or just some inspiration, our blog platform has something for everyone. Explore now and enrich your knowledge with our informative content!